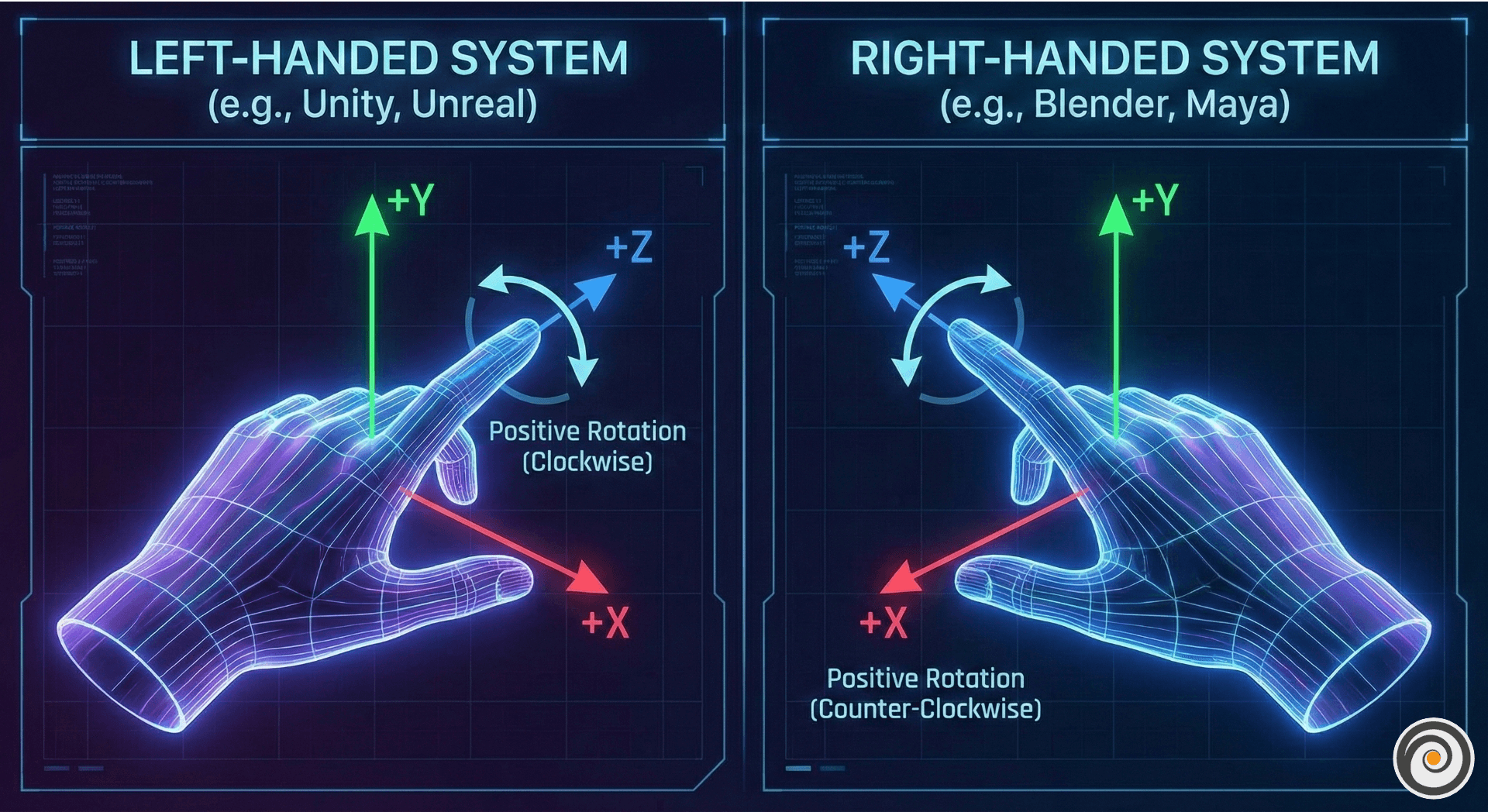
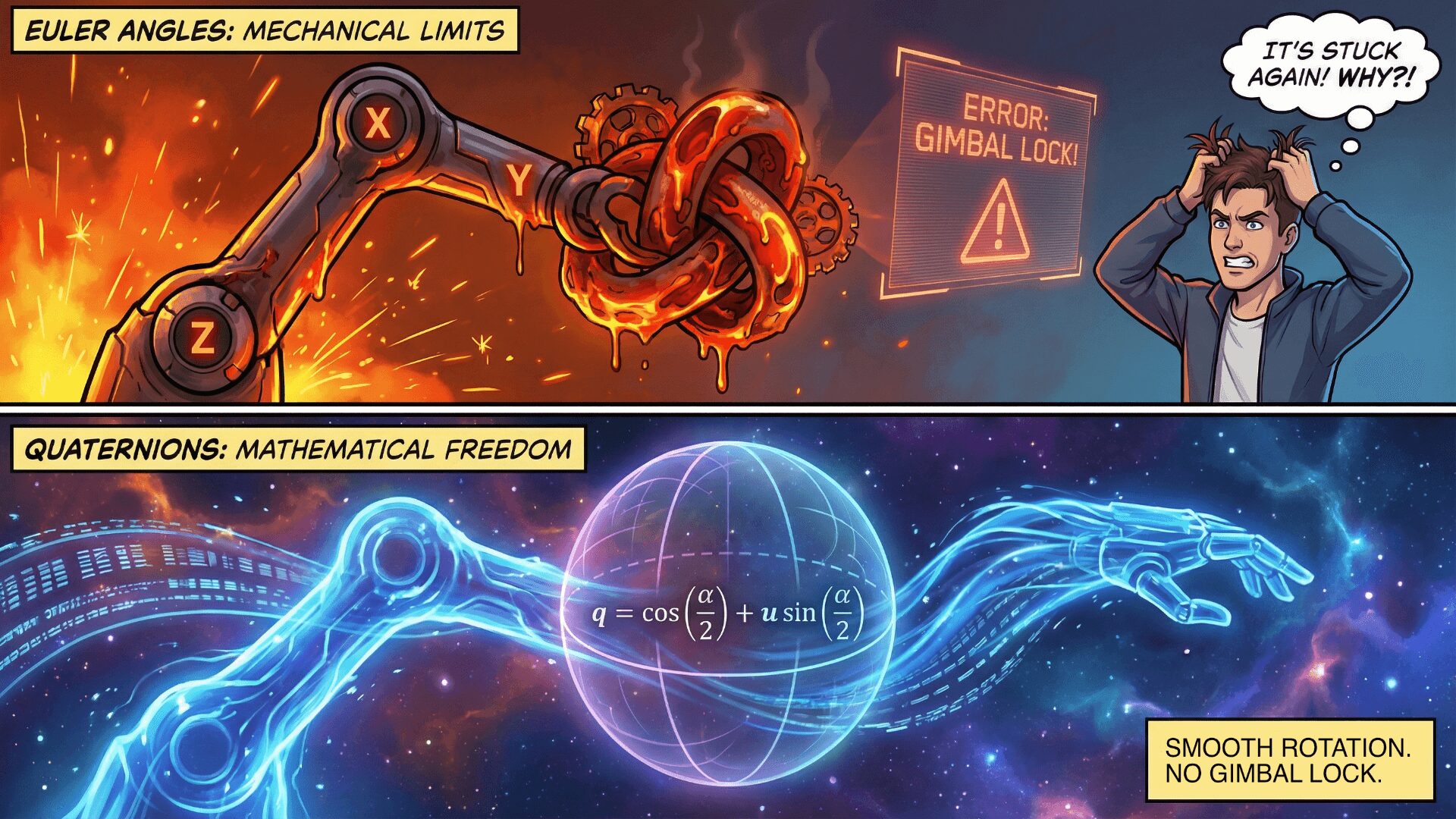
Whether you are rotating a character in Unity, calculating projectile trajectories, or building an AR/VR experience, understanding the math behind rotation is non-negotiable. While we often think in degrees, game engines and math libraries live in the world of radians.
In this post, we’ll break down everything you need to know about angles, degrees, and radians to level up your game math.
What is an Angle?
In technical terms, an angle measures the amount of rotation in a plane. In programming and math, we typically represent angles using the Greek letter θ (theta).
Degrees vs. Radians: The Two Standards
1. Degrees (°) – The Human Interface
Degrees are the standard we use in everyday life. A full rotation is 360∘.
Why 360? It is a “highly composite number,” meaning it has 22 divisors. This makes it incredibly easy to divide into halves, thirds, and quarters without needing complex fractions—a gift from ancient Babylonian mathematicians.
2. Radians (rad) – The Computer’s Language
Mathematicians and physics engines prefer radians. A radian is based on the unit circle (a circle with a radius of 1). When you measure an angle in radians, you are actually measuring the length of the arc on that unit circle.
Since the circumference of a unit circle is 2π, a full 360∘ rotation is exactly 2π radians.
How to Convert Degrees to Radians (and Vice Versa)
Most math libraries (like C# System.Math) expect radians, but your Inspector in Unity uses degrees. Use these formulas to switch between them:
Degrees to Radians Formula:
rad=deg×(180π)Radians to Degrees Formula:
deg=rad×(π180)
Pro-Tip for Unity Devs: Use
Mathf.Deg2RadandMathf.Rad2Degconstants to keep your code clean and efficient.
The Unit Circle: Understanding Sine and Cosine
If you rotate a point on a unit circle by angle θ, the resulting (x,y) coordinates are defined by Cosine and Sine. This is the secret to moving objects in a specific direction.
cos(θ)=x (Horizontal position)
sin(θ)=y (Vertical position)
Easy Memory Hack: They follow alphabetical order. X comes before Y, and Cos comes before Sin.
Essential Trig Cheat Sheet
Keep this table bookmarked for your next coding session:
| Degrees | Radians | sinθ (y) | cosθ (x) | tanθ (y/x) |
| 0° | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 |
| 30° | π/6 | 1/2 | 3 | 0.577 |
| 45° | π/4 | 2 | 2 | 1 |
| 60° | π/3 | 3 | 1/2 | 1.732 |
| 90° | π/2 | 1 | 0 | Undefined |
3 Common Mistakes to Avoid in Game Code
The “Atan” Trap: When calculating an angle from a 2D vector, always use
Atan2(y, x)instead ofAtan(y/x).Atan2handles all four quadrants correctly and avoids “Division by Zero” errors.Precision Errors: Never compare two angles using
==. Floating-point math is slightly imprecise. Instead, check if the difference is very small:if (Mathf.Abs(a - b) < 0.001f).Mixing Units: This is the #1 cause of “broken” rotations. Always verify if your function (like
Rotate()) wants degrees or radians.
Conclusion
Mastering these basics makes 3D development significantly smoother. Whether you’re working on a simple mobile app or a complex VR simulation, the relationship between angles, degrees, and radians is the foundation of everything that moves.